$ 450.0
Quantity: 1000 MG
In stock
Description
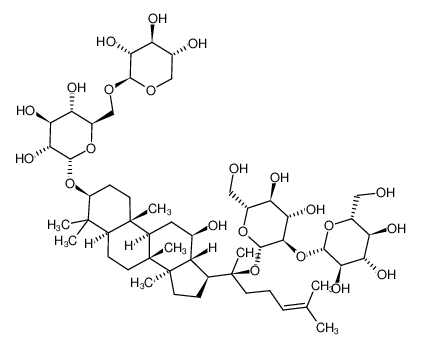
Product name: 20(R)-Ginsenoside Rg3
Synonym:
Catalog #: BP0040
Purity: 98%
CAS No.:38243-03-7
Molecular Formula: C42H72O13
Molecular Weight: 785.025
Botanical Source:Ginseng Radix Et Rhizoma
Analysis Method: HPLC-DAD or/and HPLC-ELSD
Identification Method: Mass, NMR
Packing: Brown vial or HDPE plastic bottle
Descriptions:
20(R)-Ginsenoside Rg3 has shown multiple pharmacological activities and been considered as one of the most promising approaches for fatigue treatment, however, 20(R)-Ginsenoside Rg3 has a low bioavailability after oral administration in human, so, 20(R)-Rg3 can be by intranasal administration, the mechanism was related to the increase of the storage of hepatic glycogen, and the decrease of the accumulation of metabolite such as lactic acid and serum urea nitrogen.[1]
20(R)-Ginsenoside Rg3 shows significant effect on the differential expression of cell signaling genes and other related genes in human lung cell line A549.[2]
20(R)-Ginsenoside Rg3 and PEG-PLGA-Rg3 nanoparticles can supress the tumor angiogenesis in vivo,which is perhaps related to the inhibition of expression in MMP-9,HIF-1α,VEGF,IL-1,IL-6 and TNF-α.The PEG-PLGA nanoparticles could improve Rg3’s ability on inhibiting the tumor angiogenesis in vivo.[3]
20(R)-Ginsenoside Rg3 has anticarcinogenic effects on Induced Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Rats.[4]
20(R)-Ginsenoside Rg3 elicits a significant inhibition of in vitro cell adhesion and invasion of U87 cells, is attributed to its decreasing the enzymatic activity of MMP-2.[5]
20(R)-Ginsenoside Rg3 can restrain A549/DDP cell invasion and metastasis,and it may have relationship with the upregulation of nm23;Rg3 can enhance the A549/DDP cell chemosensitivity to cisplatin,and it may have relationship with the upregulation of caspase-3 and the cell membrane lipid fluidity decreased.[6]
References:
[1] Tang W, Zhang Y, Gao J, et al. Biol Pharm Bull, 2008, 31(11):2024-7.
[2] Chen M W, Yang L, Lei N I, et al. Chinese Journal of Tuberculosis and Respiratory Diseases, 2005, 28(1):37-40.
[3] Geng L, Xing S L, Jing Y U, et al. China Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine & Pharmacy, 2014(02):601-4.
[4] Xiao L I, Guan Y S, Zhou X P, et al. Journal of Sichuan University. Medical science edition, 2005, 36(2):217-20.
[5] Liu Y, Liu X, Shi L, et al. Clinical Journal of Medical Officers, 2014, 42(11):4-7.
[6] Wang Y, Liu J L, Liu L, et al. Chinese Journal of Health Laboratory Technology, 2011(03):609-11.
[7] Tang M H, Jiang Z H, Zhao Z Z, et al. Chinese herbal medicine, 2004, 35 (03): 280-2.