$ 270.0
Quantity: 1Gram
In stock
Description
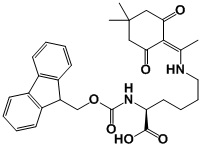
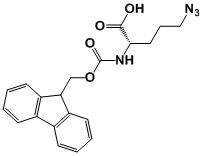
Product name: Fmoc-Lys(N3)-OH
Synonym: Fmoc-lysine azide,Fmoc-N6-diazo-L-lysine,N2-(((9H-fluoren-9-yl)methoxy)carbonyl)-N6-diazo-L-lysine,
Catalog #: 8302025
Purity: 97%
CAS No.: 159610-89-6
Molecular Formula: C21H22N4O4
Molecular Weight: 394.43
Compound ID: 25146063
Description: Azido-protected Fmoc-Lys-OH (Fmoc-Lys(N3)-OH) was synthesized from Fmoc-Lys-OH by the copper(II)-catalyzed diazo transfer method, and introduced to a peptide by the ordinary Fmoc-based solid-phase peptide synthesis. Cyclic Peptide Obtained via i to i+4 Intramolecular Side-Chain to Side-Chain Azide−Alkyne 1,3-Dipolar Cycloaddition. The solid-phase assembly of the linear precursor including ϵ-azido norleucine and the propargylglycine (Pra) in positions i and i+4, respectively, was accomplished by either subjecting the resin-bound peptide to selective on-resin diazo transformation of a Lys into the Nle(ϵ-N3) or the incorporation of Fmoc-Nle(ϵ-N3)-OH during the stepwise build-up of the resin-bound peptide. Intramolecular side-chain to side-chain cyclization is an established approach to achieve stabilization of specific conformations and a recognized strategy to improve resistance toward proteolytic degradation. To this end, cyclizations, which are bioisosteric to the lactam-type side-chain to side-chain modification and do not require orthogonal protection schemes, are of great interest. Herein, we report the employment of Cu(I)-catalyzed 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition of side chains modified with azido and alkynyl functions and explore alternative synthetic routes to efficiently generate 1,4-disubstituted [1,2,3]triazolyl-containing cyclopeptides. The solid-phase assembly of the linear precursor including epsilon-azido norleucine and the propargylglycine (Pra) in positions i and i+4, respectively, was accomplished by either subjecting the resin-bound peptide to selective on-resin diazo transformation of a Lys into the Nle(epsilon-N3) or the incorporation of Fmoc-Nle(epsilon-N3)-OH during the stepwise build-up of the resin-bound peptide.